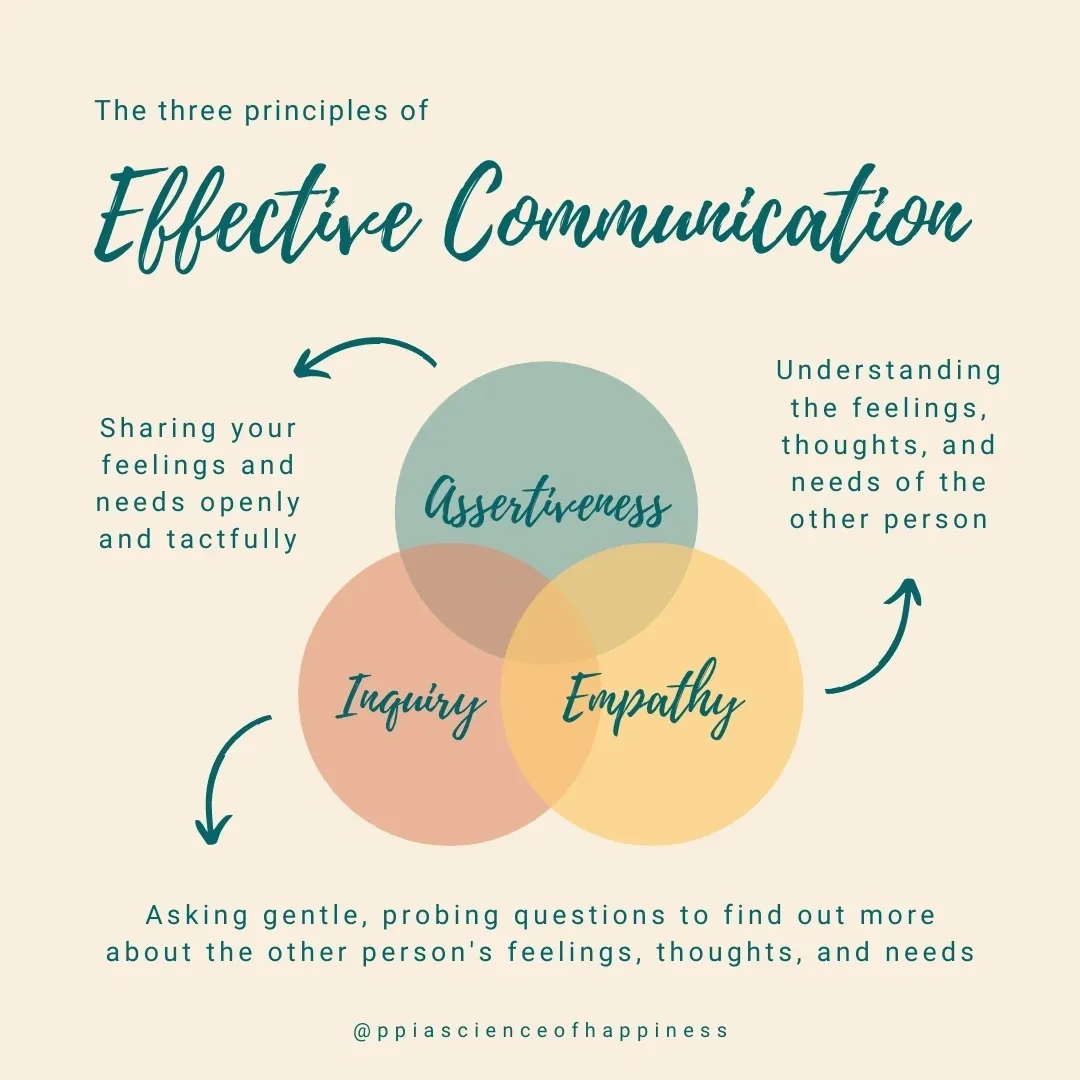
Basic principles of effective communication
Effective communication is vital in various contexts, including the workplace, personal relationships, and public interactions. Here are some basic principles of effective communication:
Clarity and Conciseness: Your message should be clear and to the point. Avoid unnecessary jargon, ambiguity, and overly complex language. Be concise in your wording so that your message is easily understood.
Active Listening: Effective communication is not just about speaking; it’s also about listening. Active listening involves paying close attention to what the other person is saying, understanding their message, and responding thoughtfully.
Empathy and Understanding: Try to understand where the other person is coming from. Put yourself in their shoes to appreciate their perspective. This helps in responding appropriately and building a rapport.
Non-Verbal Cues: Pay attention to non-verbal signals, such as body language, eye contact, and tone of voice. These can often convey more than words and are crucial for understanding the full message.
Feedback: Encourage and provide feedback. This can confirm that your message has been understood as intended and allows for adjustments if necessary.
Respect and Tolerance: Show respect for the opinions and perspectives of others, even if they differ from your own. A respectful approach fosters open and honest communication.
Adaptability: Be adaptable in your communication style. Different situations and audiences may require different approaches. For instance, the way you communicate with colleagues might differ from how you communicate with clients.
Cultural Sensitivity: Be aware of cultural differences in communication styles and practices. What might be considered polite or straightforward in one culture could be perceived differently in another.
Clarity of Purpose: Have a clear purpose for your communication. Knowing what you want to achieve with your message can guide the way you convey it.
Consistency: Ensure your messages are consistent, especially in a professional setting. Inconsistent messages can lead to confusion and mistrust.
Emotional Intelligence: Be aware of the emotions behind your words and also those of the person you are communicating with. Emotional intelligence can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your communication.
Use of Technology: In today’s digital age, understand how to effectively use different communication technologies (like email, social media, video conferencing) to enhance, not hinder, your message.
Practicing these principles can greatly improve your ability to communicate effectively in various situations, leading to better understanding, reduced conflicts, and more productive interactions.