Generating Ideas
Brainstorming Techniques: Creative Problem Solving
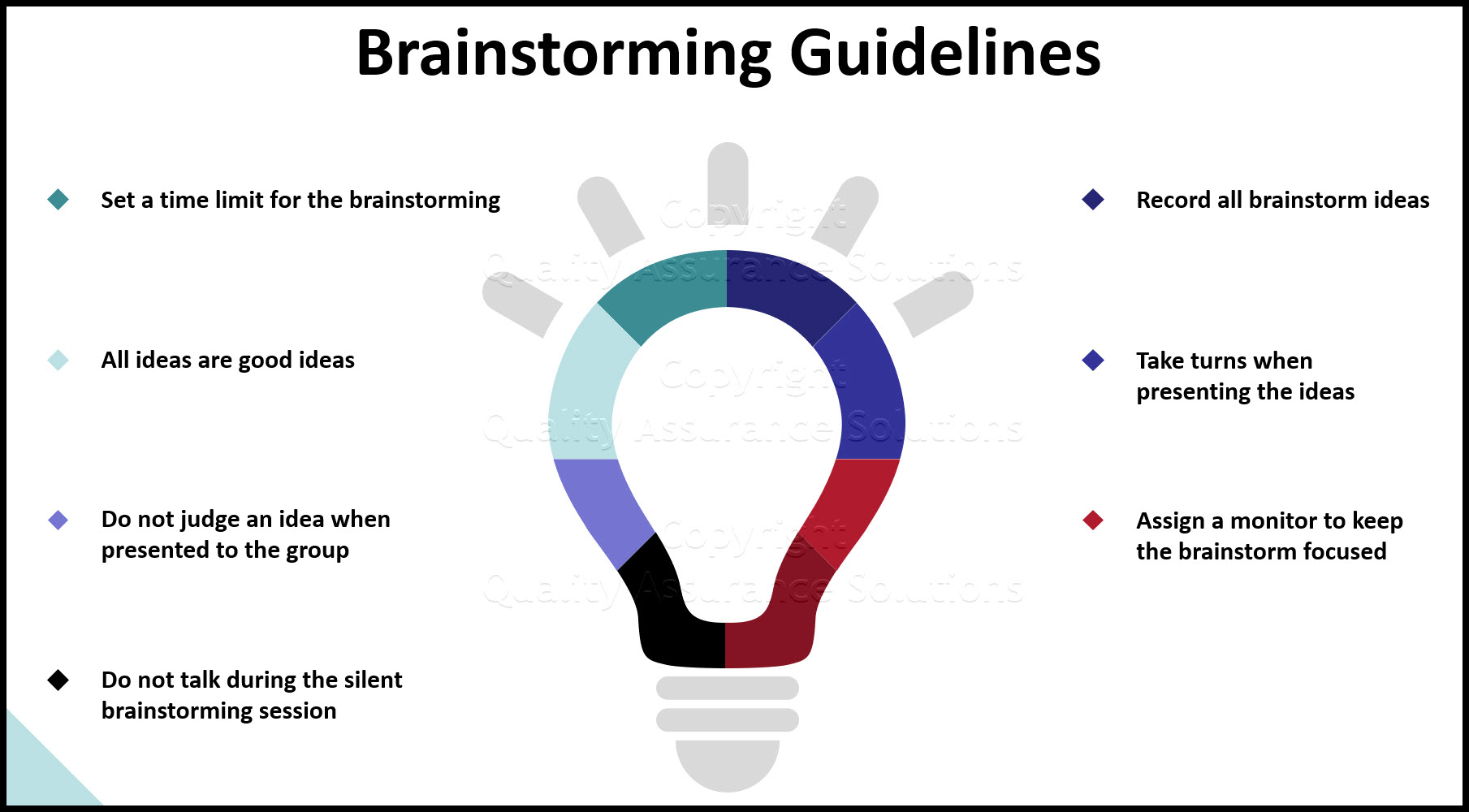
Brainstorming is a vital component of the Creative Problem Solving (CPS) process, enabling teams to generate a wide range of ideas and solutions. Various techniques can be employed to enhance creativity and ensure effective idea generation. Here are several effective brainstorming techniques that can be utilized in business settings:
1. Brainwriting
Brainwriting is a nonverbal brainstorming method that allows participants to write down their ideas individually before sharing them with the group.
- How It Works: Each participant writes down three ideas related to the topic within a set time frame (e.g., four to six minutes). After this, they pass their ideas to the person on their right (or left), who builds upon those ideas by adding bullet points or additional thoughts. This process continues until all ideas have circulated.
- Benefits: This technique mitigates common pitfalls such as unbalanced conversation and the anchoring effect, ensuring everyone contributes and reducing bias toward initial ideas
2. Rapid Ideation
Rapid ideation focuses on generating as many ideas as possible within a constrained time frame.
- How It Works: Participants write down their ideas quickly without discussion or critique. A time limit is set (e.g., 10 minutes), creating a sense of urgency that encourages spontaneous thinking.
- Benefits: This technique prevents premature judgment of ideas, allowing participants to explore creative thoughts freely before any evaluation takes place
3. Figure Storming
Figure storming involves imagining how a well-known figure would approach a problem.
- How It Works: The team selects a public figure, fictional character, or leader and discusses how that person might tackle the challenge at hand. For example, “How would Steve Jobs approach this product launch?”
- Benefits: This technique helps break down barriers to creative thinking by allowing participants to step outside their own perspectives and consider alternative viewpoints.
4. Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual brainstorming technique that organizes thoughts and ideas around a central concept.
- How It Works: Start with a central idea written in the middle of a page, then branch out with related sub-ideas connected by lines. Each branch can further develop into more specific concepts.
- Benefits: Mind mapping encourages visual thinkers to explore connections between ideas and can help prevent the anchoring effect by allowing multiple pathways of thought
5. Starbursting
Starbursting is an exploratory brainstorming technique focused on generating questions rather than answers.
- How It Works: Place the main idea at the center of a star diagram, labeling each point with the 5Ws and H (Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How). Develop questions related to each point.
- Benefits: This method encourages thorough exploration of an idea’s implications and potential challenges, leading to more robust strategies
6. Round Robin Brainstorming
Round robin brainstorming ensures that all team members contribute equally during idea generation.
- How It Works: Participants sit in a circle and take turns sharing one idea at a time in response to a prompt. No discussion or critique occurs until everyone has contributed.
- Benefits: This technique promotes balanced participation and ensures that quieter team members have an opportunity to share their thoughts without interruption
7. Crazy 8s
Crazy 8s is a fast-paced brainstorming technique designed for rapid idea generation.
- How It Works: Each participant folds a piece of paper into eight sections and has eight minutes to sketch eight different ideas related to the topic.
- Benefits: This method encourages quick thinking and helps participants move past initial ideas, often leading to unexpected insights.
8. SCAMPER Technique
SCAMPER is an acronym for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse.
- How It Works: Teams apply each SCAMPER prompt to an existing idea or product to explore new possibilities:
- Substitute something in the process or product.
- Combine two elements for synergy.
- Adapt features from other products.
- Modify aspects for improvement.
- Put the idea to another use.
- Eliminate unnecessary components.
- Reverse processes or approaches.
- Benefits: SCAMPER provides structured prompts that encourage innovative thinking by challenging existing assumptions about products or processes.
9. Charette Technique
The charette technique divides larger groups into smaller teams that address different aspects of a problem.
- How It Works: Each small group brainstorms solutions for a specific aspect of the problem in separate rooms. After a set time, groups rotate rooms and build upon the previous group’s ideas.
- Benefits: This method allows for focused discussions on various components of complex issues while leveraging collective insights from multiple groups.
Conclusion
Implementing diverse brainstorming techniques enhances creativity and collaboration within teams during the CPS process. By utilizing methods such as brainwriting, rapid ideation, figure storming, mind mapping, starbursting, round robin brainstorming, Crazy 8s, SCAMPER, and the charette technique, organizations can foster an environment where innovative solutions thrive. These techniques not only promote idea generation but also ensure that all voices are heard in the creative process, ultimately leading to more effective problem-solving outcomes.
Brainstorming Techniques: Mind Mapping as a Tool for Idea Generation
Mind mapping is a powerful visual technique that enhances idea generation by organizing thoughts and concepts in a non-linear format. This method allows individuals and teams to explore ideas freely, making it an effective tool for brainstorming and creative problem-solving. Below is an elaboration on how mind mapping works, its benefits, and practical applications in various business contexts.
What is Mind Mapping?
Mind mapping involves starting with a central concept or idea and branching out into related thoughts, categories, or factors. Each branch represents a sub-idea that connects back to the main topic, creating a visual representation of the relationships between different concepts. This technique encourages free association and helps participants see connections that may not be immediately apparent in linear formats.
Key Steps in Creating a Mind Map
- Start with a Central Idea: Place the main concept in the center of the page. This could be a problem statement, project title, or any primary focus area.
- Branch Out: Draw branches radiating from the central idea to represent major categories or themes related to it. Use keywords or short phrases to label each branch.
- Add Sub-Branches: For each main branch, add sub-branches that delve deeper into specific aspects of the idea. This hierarchical structure allows for detailed exploration of each category.
- Use Colors and Images: Incorporate colors, images, and symbols to enhance visual appeal and facilitate memory retention. Different colors can represent different themes or levels of importance.
- Review and Revise: After completing the initial mind map, review it for clarity and coherence. Revise as necessary to ensure that all relevant ideas are included and organized logically.
Benefits of Mind Mapping for Idea Generation
- Enhanced Creativity: Mind mapping encourages free-flowing thought without the constraints of linear thinking. Participants can generate numerous ideas quickly, fostering a creative environment where unconventional solutions can emerge.
- Visual Organization: The visual nature of mind maps helps individuals see relationships between ideas more clearly than traditional lists or outlines. This organization aids in understanding complex topics and identifying connections.
- Increased Engagement: Mind mapping can be more engaging than conventional brainstorming sessions. The interactive nature of creating a mind map encourages participation from all team members, promoting collaboration and diverse input.
- Flexibility: Mind maps are adaptable; they can be easily modified as new ideas arise or as discussions evolve. This flexibility allows teams to pivot quickly during brainstorming sessions.
- Facilitation of Memory Retention: The combination of images, colors, and structured information enhances memory retention, making it easier for participants to recall ideas generated during the session.
Practical Applications of Mind Mapping in Business
- Project Planning: Teams can use mind maps to outline project objectives, tasks, timelines, and responsibilities, providing a clear visual overview of project components.
- Problem Solving: When faced with complex challenges, mind mapping helps teams explore potential solutions by breaking down problems into manageable parts and identifying root causes.
- Strategic Planning: Organizations can utilize mind mapping to visualize strategic goals, market analysis, competitive positioning, and action plans in one cohesive diagram.
- Content Development: Writers can create mind maps to organize ideas for articles, reports, or presentations, ensuring that all relevant points are covered systematically.
- Training and Workshops: Facilitators can employ mind mapping during training sessions to encourage participant engagement and capture insights from group discussions effectively.
- Marketing Campaigns: Marketing teams can brainstorm campaign ideas using mind maps to explore target audiences, messaging strategies, channels, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Conclusion
Mind mapping is an invaluable tool for idea generation that enhances creativity, promotes collaboration, and organizes thoughts visually. By employing this technique in various business contexts—such as project planning, problem-solving, strategic planning, content development, training sessions, and marketing campaigns—organizations can foster an innovative culture that drives success. The flexibility and effectiveness of mind mapping make it an essential component of the Creative Problem Solving (CPS) process that empowers teams to generate impactful solutions efficiently.
Encouraging Creativity: Techniques to Foster a Creative Mindset Among Teams
Fostering a creative mindset within teams is essential for driving innovation and problem-solving in any organization. By creating an environment that encourages creative thinking, teams can generate novel ideas, adapt to challenges, and enhance overall performance. Here are several effective techniques to cultivate a creative mindset among team members:
1. Build a Culture of Trust and Psychological Safety
Creating an environment where team members feel safe to express their ideas without fear of judgment is crucial for fostering creativity. Psychological safety encourages open dialogue and risk-taking.
- Implementation: Encourage team members to share their thoughts freely during meetings. Leaders should model vulnerability by sharing their own ideas and acknowledging mistakes. Regularly emphasize that all contributions are valued, regardless of their feasibility.
2. Encourage Brainstorming and Idea Generation
Structured brainstorming sessions can stimulate creativity by allowing team members to explore ideas collaboratively.
- Implementation: Set clear objectives for brainstorming sessions and use facilitators to guide discussions. Encourage unconventional thinking by allowing “wild” ideas that can be refined later. Record all ideas generated, ensuring everyone has a chance to contribute.
3. Provide Opportunities for Skill Development
Investing in training and development can enhance team members’ creative skills and boost their confidence in applying them.
- Implementation: Offer workshops on creative thinking techniques such as mind mapping, SCAMPER, or design thinking. Encourage cross-functional collaboration to expose team members to diverse perspectives and skill sets.
4. Foster a Growth Mindset
Encouraging a growth mindset helps teams view challenges as opportunities for learning rather than obstacles.
- Implementation: Promote the idea that abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work. Recognize effort and progress, not just outcomes, to reinforce this mindset.
5. Offer Flexibility and Autonomy
Creativity flourishes when individuals have the freedom to explore their ideas without rigid constraints.
- Implementation: Allow team members to set their own schedules or work on projects they are passionate about. Encourage experimentation with new approaches and give them the autonomy to pursue innovative solutions.
6. Create Collaborative Spaces
Physical and virtual environments that promote collaboration can enhance creativity among team members.
- Implementation: Design open office layouts or create dedicated spaces for brainstorming sessions equipped with tools like whiteboards, sticky notes, and digital collaboration platforms. Encourage informal gatherings where team members can share ideas casually.
7. Encourage Knowledge Sharing
Facilitating knowledge sharing among team members fosters creativity by exposing them to new ideas and perspectives.
- Implementation: Organize regular knowledge-sharing sessions where team members present on topics of interest or recent learnings. Create digital platforms for sharing articles, resources, or insights related to industry trends.
8. Recognize and Reward Creativity
Acknowledging and rewarding creative contributions motivates team members to continue thinking outside the box.
- Implementation: Implement recognition programs that celebrate innovative ideas or successful projects. Offer both intrinsic rewards (personal satisfaction) and extrinsic rewards (public recognition or bonuses) to reinforce creative efforts.
9. Inspire Curiosity
Curiosity drives creativity by encouraging exploration and experimentation.
- Implementation: Foster a culture where asking questions is encouraged. Provide opportunities for team members to explore new subjects through workshops, guest speakers, or industry conferences.
10. Implement Innovative Problem-Solving Techniques
Introduce structured creative problem-solving methods that guide teams through the ideation process.
- Implementation: Techniques like design thinking, SCAMPER, or the “Yes, And…” approach from improvisational theater can help teams think creatively about challenges while ensuring they remain focused on actionable solutions.
Conclusion
By implementing these techniques, organizations can cultivate a creative mindset among their teams, leading to enhanced innovation and problem-solving capabilities. Creating an environment that values trust, collaboration, autonomy, curiosity, and recognition will empower team members to explore new ideas fearlessly and contribute meaningfully to the organization’s success. Fostering creativity is not just about generating ideas; it’s about building a culture that embraces change and encourages continuous improvement across all levels of the organization.
Encouraging Creativity: Overcoming Barriers to Creativity
Creativity is essential for innovation, problem-solving, and organizational growth. However, various barriers can hinder creative thinking and the generation of innovative ideas. Understanding these barriers and implementing strategies to overcome them is crucial for fostering a creative environment. Below are common barriers to creativity and techniques to address them effectively.
1. Fear of Failure
One of the most significant barriers to creativity is the fear of failure. Team members may hesitate to share their ideas due to concerns about being judged or ridiculed.
- Overcoming the Barrier:
- Create a Safe Environment: Foster a culture where failure is viewed as a learning opportunity rather than a setback. Encourage team members to share their ideas without fear of criticism.
- Celebrate Experimentation: Recognize and reward attempts at innovation, even if they do not lead to successful outcomes. This reinforces the idea that taking risks is a valuable part of the creative process.
2. Rigid Thinking and Established Norms
Many organizations operate within established frameworks and routines that can stifle creativity. When teams rely too heavily on past experiences or conventional wisdom, they may overlook innovative solutions.
- Overcoming the Barrier:
- Encourage Divergent Thinking: Promote brainstorming sessions that prioritize quantity over quality, allowing for wild and unconventional ideas. Techniques such as mind mapping can help visualize connections between different concepts.
- Challenge Assumptions: Regularly question existing practices and encourage team members to think critically about why things are done a certain way. This can lead to fresh perspectives and innovative approaches.
3. Resource Constraints
Limited time, budget, or materials can discourage creative thinking, leading teams to believe that innovative ideas are impractical.
- Overcoming the Barrier:
- View Constraints as Opportunities: Encourage teams to see resource limitations as challenges that can stimulate creativity. Use techniques like SCAMPER (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse) to generate ideas within constraints.
- Rapid Prototyping: Implement fast prototyping methods that allow teams to test ideas quickly with minimal resources. This approach encourages experimentation and iterative learning.
4. Lack of Clarity
When teams lack a clear understanding of the problem or goal, it becomes difficult to generate relevant ideas.
- Overcoming the Barrier:
- Define Problems Clearly: Use problem statements or frameworks to clarify objectives before brainstorming sessions. Ensure that all team members have a shared understanding of the challenge at hand.
- Set Success Criteria: Establish clear criteria for evaluating ideas so that team members know what outcomes are desired. This helps focus discussions and encourages relevant contributions.
5. Inadequate Collaboration
Creativity thrives in collaborative environments where diverse perspectives are valued. However, silos within organizations can limit interaction among team members.
- Overcoming the Barrier:
- Encourage Cross-Functional Teams: Form diverse teams with members from different departments or backgrounds to bring varied viewpoints into the creative process.
- Facilitate Open Communication: Implement tools and platforms that promote collaboration, such as digital brainstorming boards or regular check-in meetings where team members can share insights.
6. Time Constraints
In fast-paced work environments, employees may feel they lack time for creative thinking due to competing priorities.
- Overcoming the Barrier:
- Allocate Time for Creativity: Designate specific times for brainstorming or creative thinking sessions within the work schedule. Encourage employees to set aside time in their calendars for innovation-related activities.
- Integrate Creativity into Daily Routines: Foster habits that incorporate creative thinking into everyday tasks, such as encouraging team members to reflect on challenges during meetings or take short breaks for idea generation.
Conclusion
Overcoming barriers to creativity is essential for fostering an innovative culture within organizations. By addressing fears of failure, rigid thinking patterns, resource constraints, lack of clarity, inadequate collaboration, and time constraints, organizations can create an environment where creativity flourishes. Implementing these strategies not only enhances individual and team creativity but also drives organizational growth and adaptability in an ever-changing business landscape. Encouraging a mindset that embraces experimentation and values diverse perspectives will empower teams to generate innovative solutions that lead to lasting success.